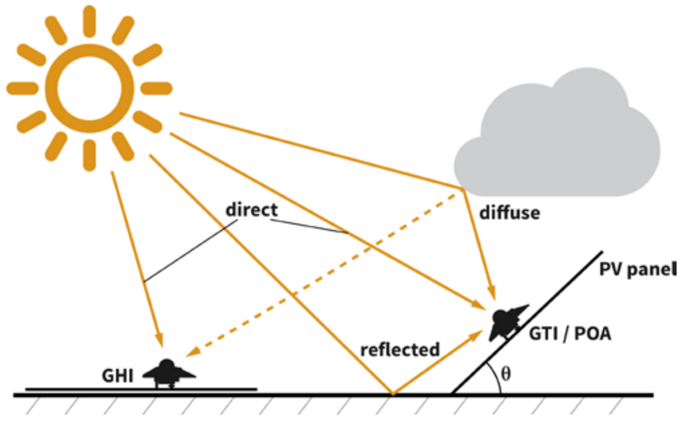
Hourly Irradiance: GHI vs POA
🔹GHI – Global Horizontal Irradiance
The total solar irradiance received on a flat, horizontal surface. Includes:
-
Direct beam radiation (projected onto the horizontal plane)
-
Diffuse sky radiation
-
Ground-reflected radiation (albedo)
→ Used as a reference for comparing site conditions.
🔹 POA – Plane of Array
The total solar irradiance received on the tilted surface of a photovoltaic (PV) module.
It includes:
-
Direct irradiance projected at the actual angle of incidence
-
Diffuse sky irradiance, adjusted for the tilt and orientation
-
Ground-reflected irradiance (albedo), depending on ground reflectivity and panel height
POA irradiance is directly affected by:
-
Panel tilt and azimuth
-
Solar geometry (sun position throughout the day/year)
-
Local shading from surrounding objects or terrain
→ It is the most relevant input for assessing actual system performance and is used in PR (Performance Ratio) calculations.
🔹 In Dashboard
Depending on the site configuration:
-
The site reference orientation may differ from the actual POA. In such cases, GHI (horizontal irradiance) is typically used as a standard reference across all sites to enable consistent performance comparisons. It is also used in site-level PR calculations.
-
The inverter orientation corresponds to the actual POA. This irradiance is used for inverter-level PR calculations, as it reflects the real exposure of the modules.
![Dashboard_header_wb.png]](https://dashboard-kb.wpo.eu/hs-fs/hubfs/Dashboard_header_wb.png?height=50&name=Dashboard_header_wb.png)